DESCRIBING COLOUR
Hue
A wedge of colour on the colour wheel. Can be called Hue Family or Colour Family. Can be any variation within that family.
Saturation
Intensity/vibrancy of a colour.
Value
Lightness or darkness of a colour.
COLOUR HARMONIES
Primary colours
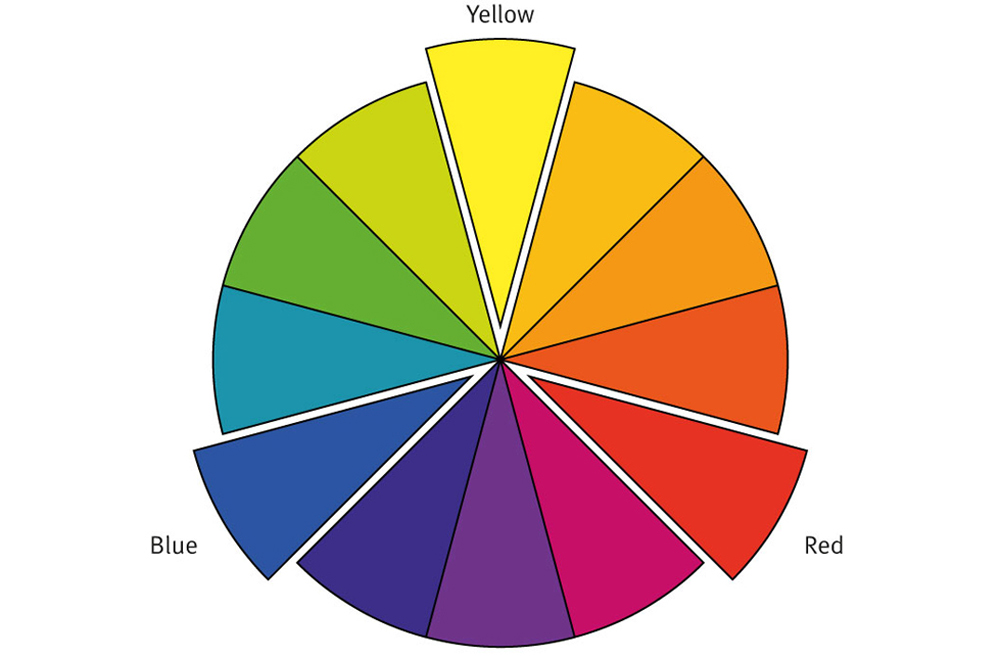
Red, yellow and blue are the three primary colours from which all other colours are made.
Secondary colours
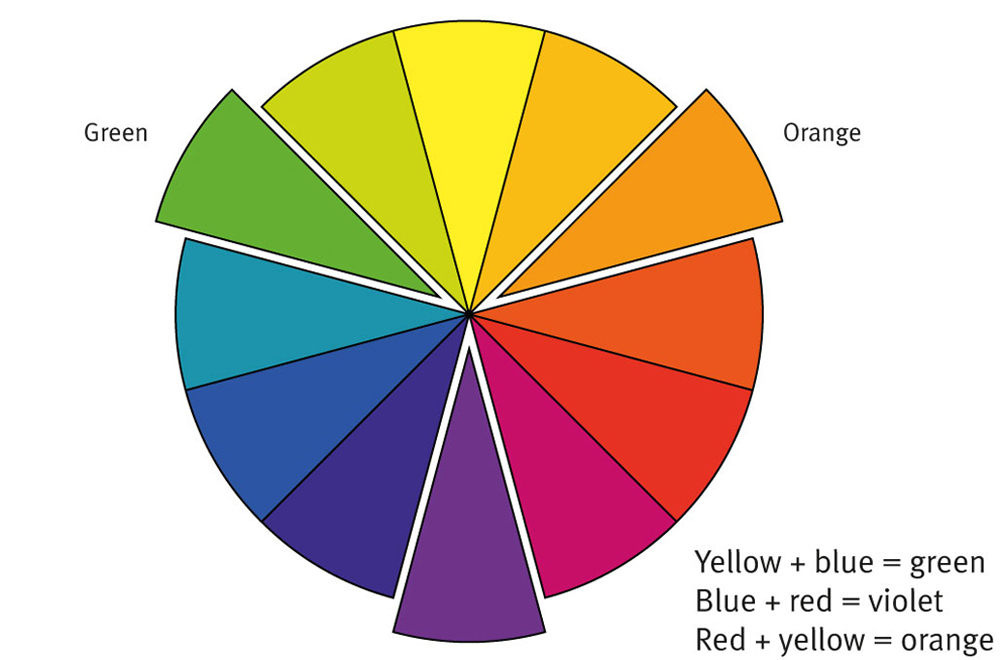
When two primary colours are mixed together they form a secondary colour:
Yellow + blue = green
Blue + red = violet
Red + yellow = orange
Tertiary colours
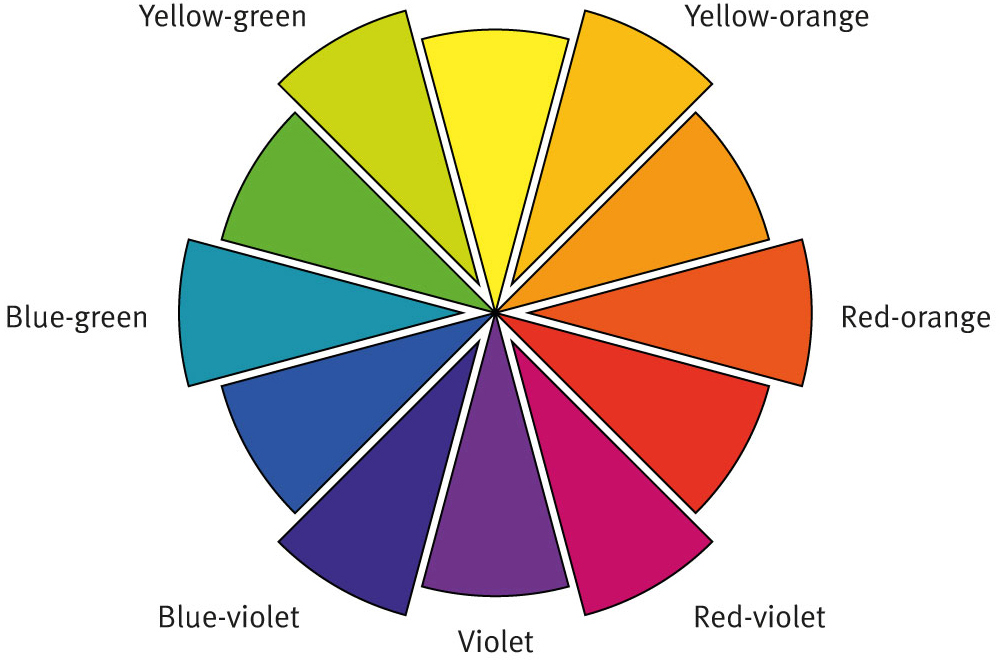
When one primary colour and its adjacent secondary colour are mixed together they form a tertiary colour:
Yellow + orange = yellow-orange
Yellow + green = yellow-green
Blue + green = blue-green
Blue + violet = blue-violet
Red + violet = red-violet
Red + orange = red-orange
Complementary colours
Lie directly opposite each other on the colour wheel.
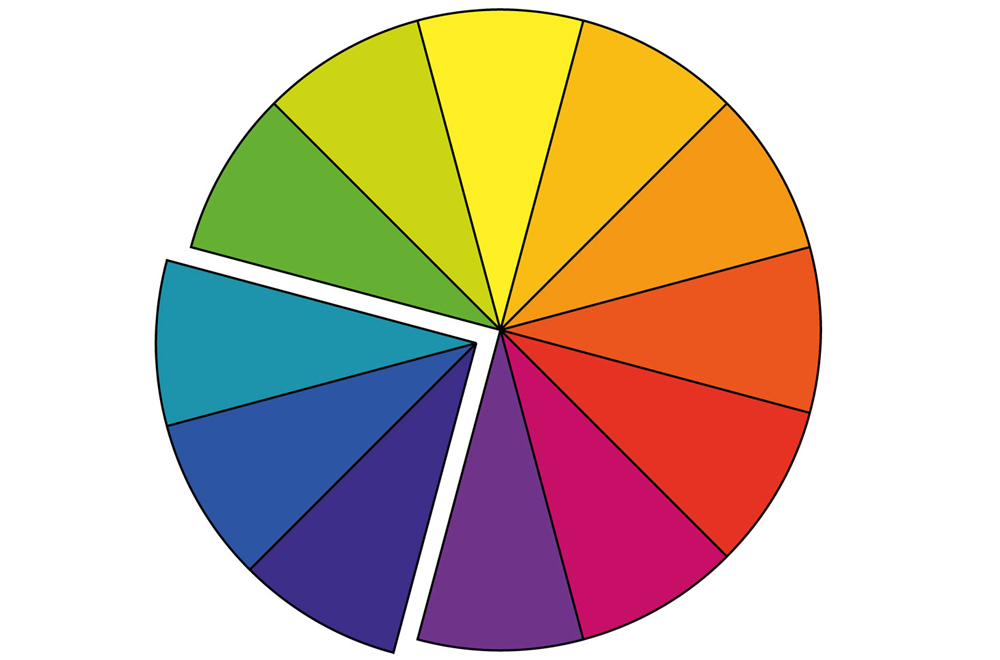
Analogous colours
Found close together on the colour wheel, usually within one quarter of the wheel.
Warm/cool colours
One half of the colour wheel has warm colours and the other half cool:
Warm: Yellow-green through orange to red inclusive
Cool: Red-violet through blue to green inclusive
Tints, tones and shades
White + colour = tint
Grey + colour = tone
Black + colour = shade
Neutrals
Black, white, greys and browns.
Monochromatic colours
Mono = one, chroma = colour
Monochromatic colours are the various tints, tones and shades of a particular hue.
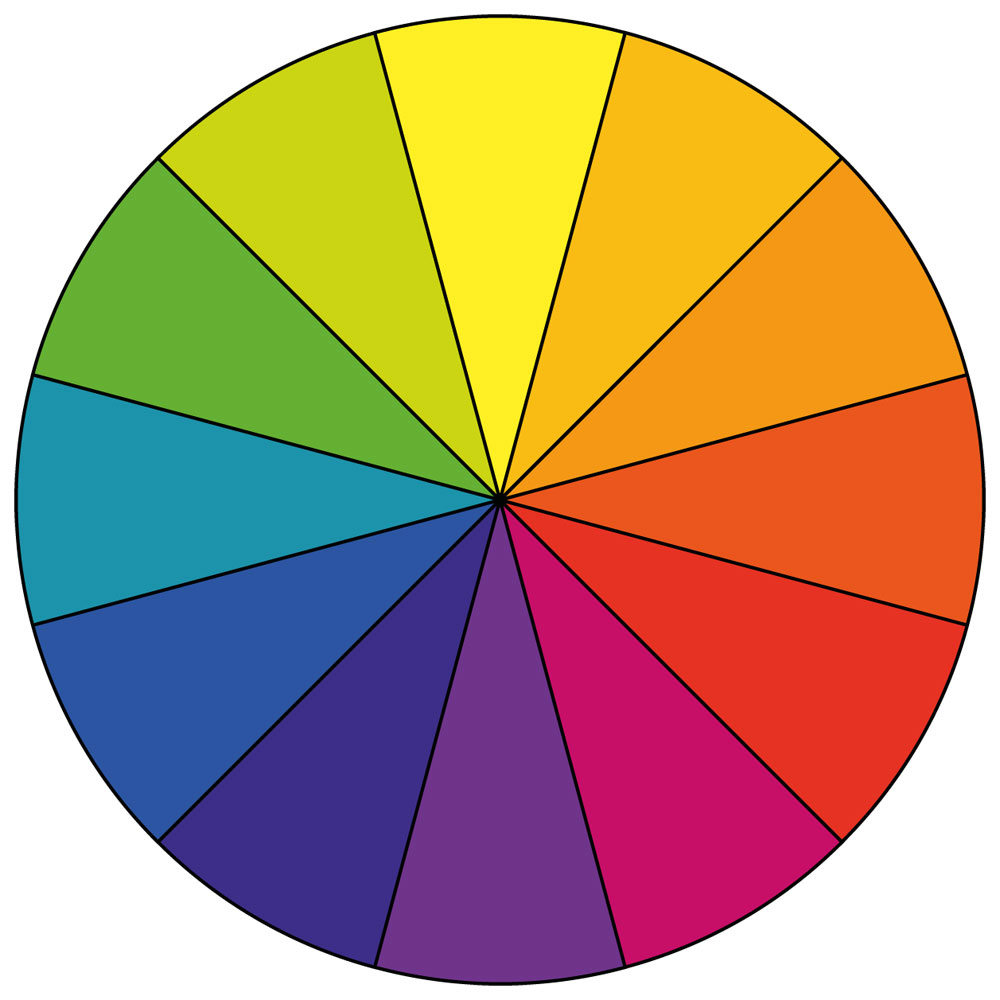
PRIMARY COLOURS
The colour wheel has three primary colours – yellow, red, blue – from which all other colours are mixed.
SECONDARY COLOURS
When two primary colours are mixed together, they create a secondary colour.
TERTIARY COLOURS
When a secondary colour and its adjacent primary are mixed, they create a tertiary colour. You can make exciting and rich blends because you get to use a minimum of six colours, every second colour on the wheel.
Primary + Secondary = Tertiary
Blue + violet = blue-violet
Blue + green = blue-green
Yellow + green = yellow-green
Yellow + orange = yellow-orange
Red + orange = red-orange
Red + violet = red-violet
In multi-coloured dyeings, cool colours recede and warm colours come forward.
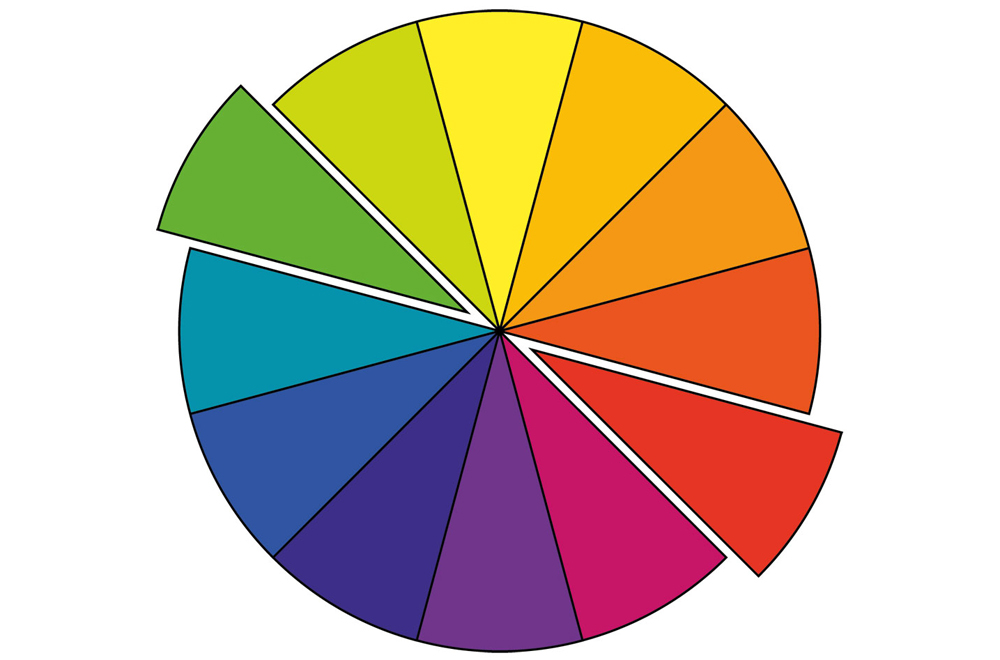
COMPLEMENTARY COLOURS
A complementary blend uses two hues that lie directly opposite You only have to step out into the garden to be inspired by nature’s perfection at using this harmony.
ANALOGOUS COLOURS
Analogous colours are those which are close to each other on the colour wheel, usually including three hues.
Dye Colour Theory
Click to download printable PDF
Click to view dyeing tutorials
For detailed material safety data, full dye instructions, colour recipes and advice.